The Dolt for Beginners series focuses on topics people getting started with Dolt will likely be interested in. Most of our other blog articles go pretty deep so we want a space to talk about topics that experts may find boring.

Dolt is a Structured Query Language (SQL) database. SQL databases have been around since the early 1970s, over 50 years now! SQL is still the most popular language used to interact with data. In SQL databases, data is structured in tables retrieved with SELECT queries and modified with INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE queries. There’s a lot to cover for a beginner to SQL when using Dolt. But, SQL is an essential tool in almost any engineer’s toolkit.
If you haven’t read the schema beginner’s article or the beginner’s SELECT article, I would start there. This article assumes you already have a schema and covers basic SQL INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE queries used to modify data in an existing Dolt database.
Download and Install the Workbench#
The Dolt Workbench is the easiest way for Beginners to get started with Dolt. It is a graphical user interface that doesn’t require a terminal to get started. Install it.
The Dolt Workbench is a standard desktop application. It is available in both the Mac and Windows App Stores or you can download the appropriate installer from GitHub.
Once you have it installed launch it like you would launch any other Desktop application.
After starting the Dolt Workbench you are prompted to connect to a database server. The Dolt Workbench works with any MySQL- or Postgres-compatible database.
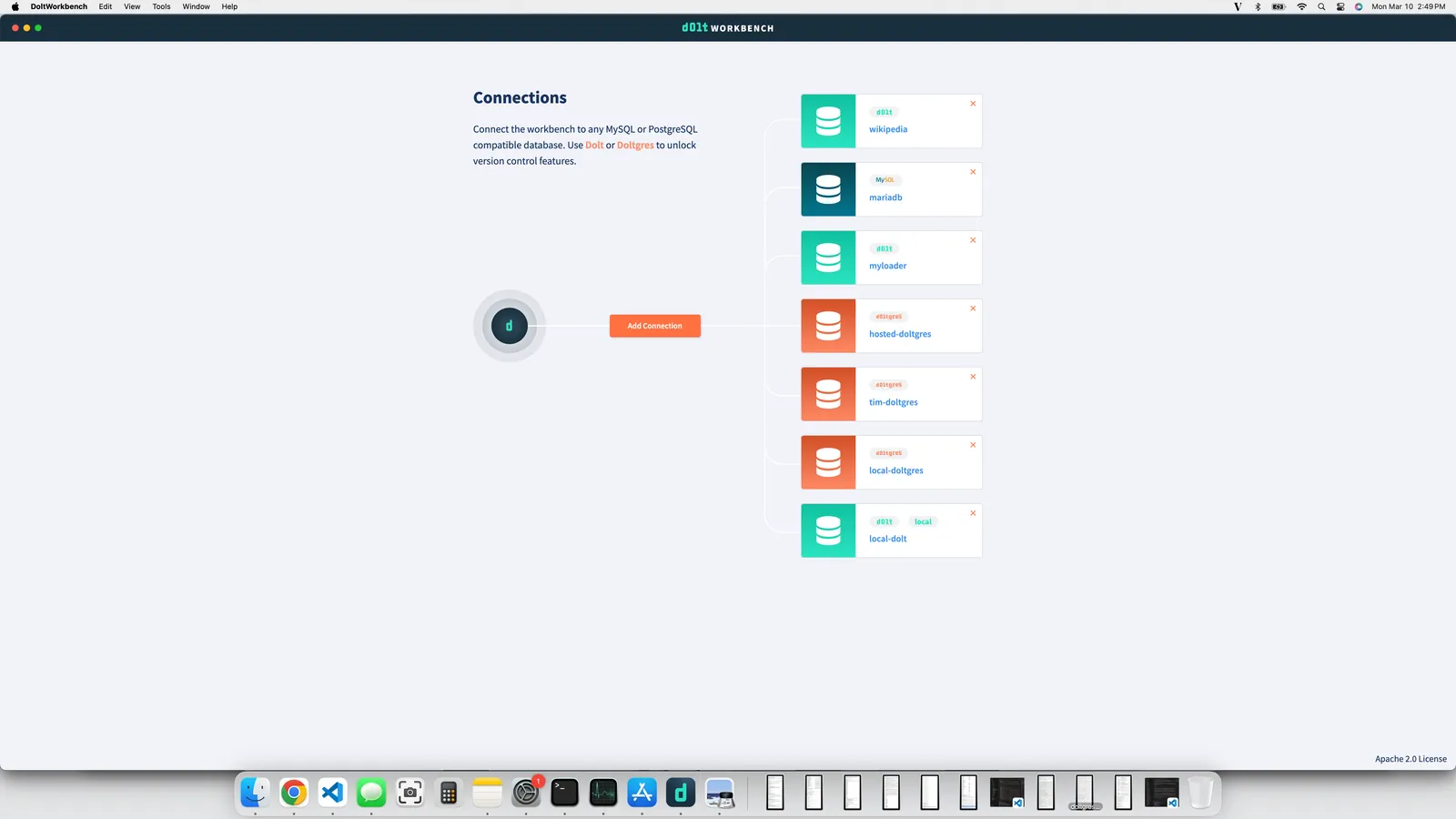
I have a bunch of connections to various databases but you won’t have one as a beginner. So click the “Add Connection” button. We’re going to start a local SQL server and select the option to clone a database from DoltHub. This will download a database from DoltHub for us to practice our SQL on. For this article I created a database called timsehn/iud. “iud” stands for “insert update delete”. We won’t have to create a database from scratch which is pretty cool if you ask me.
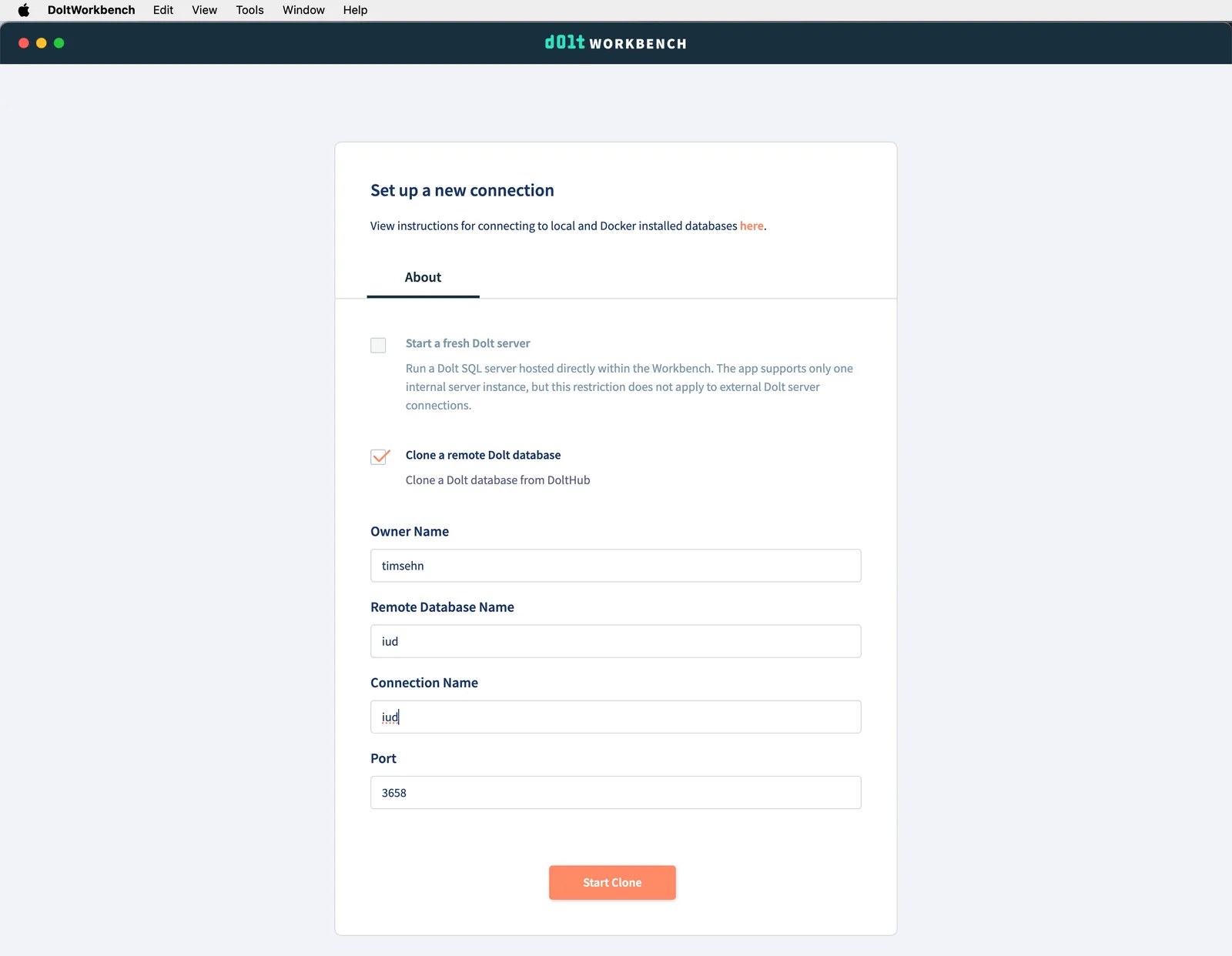
Click “Start Clone” and you should see timsehn/iud. It should download pretty quickly because the database is very small. Once it completes you will have a database to play with.
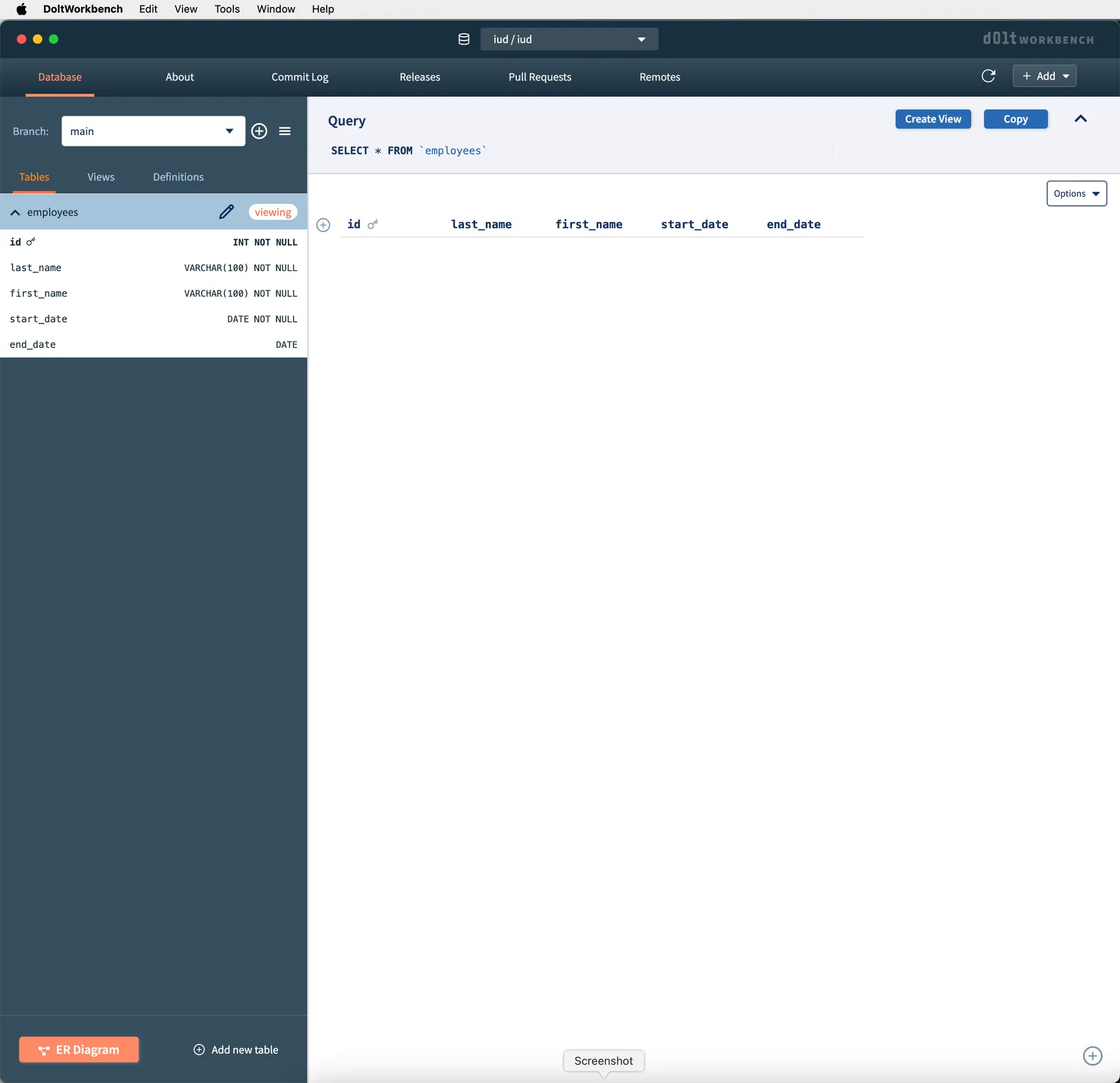
The database has a single, empty table called employee with four columns first_name, last_name, start_date and end_date. It’s the type of table you would see in Employee Resource Planning (ERP) applications. We’re going to insert and modify data in this table using SQL.
Insert#
The first thing we need to do is insert some data into this table. We do this with the aptly named INSERT SQL statement. Insert statements take the general form:
INSERT INTO <table>(<column>, <column>, ...) VALUES (<value>, <value>, ...);Let’s insert three employees into the table. We will do this with three separate insert statements.
INSERT into employees(last_name, first_name, start_date) values ('Sehn', 'Tim', '2018-08-04');
INSERT into employees(last_name, first_name, start_date) values ('Hendriks', 'Brian', '2018-08-04');
INSERT into employees(last_name, first_name, start_date) values ('Son', 'Aaron', '2018-08-04');A couple things to note here. The values are in single quotes because they are strings, not numbers. We are not inserting an end_date because that means we all still work at DoltHub.
I enter these queries one at a time into the Dolt Workbench query box and click play after each one. The Dolt Workbench shows my table grow via the diff view after each query. Believe it or not, Dolt is the only SQL database that can show you diffs of what you’ve changed.
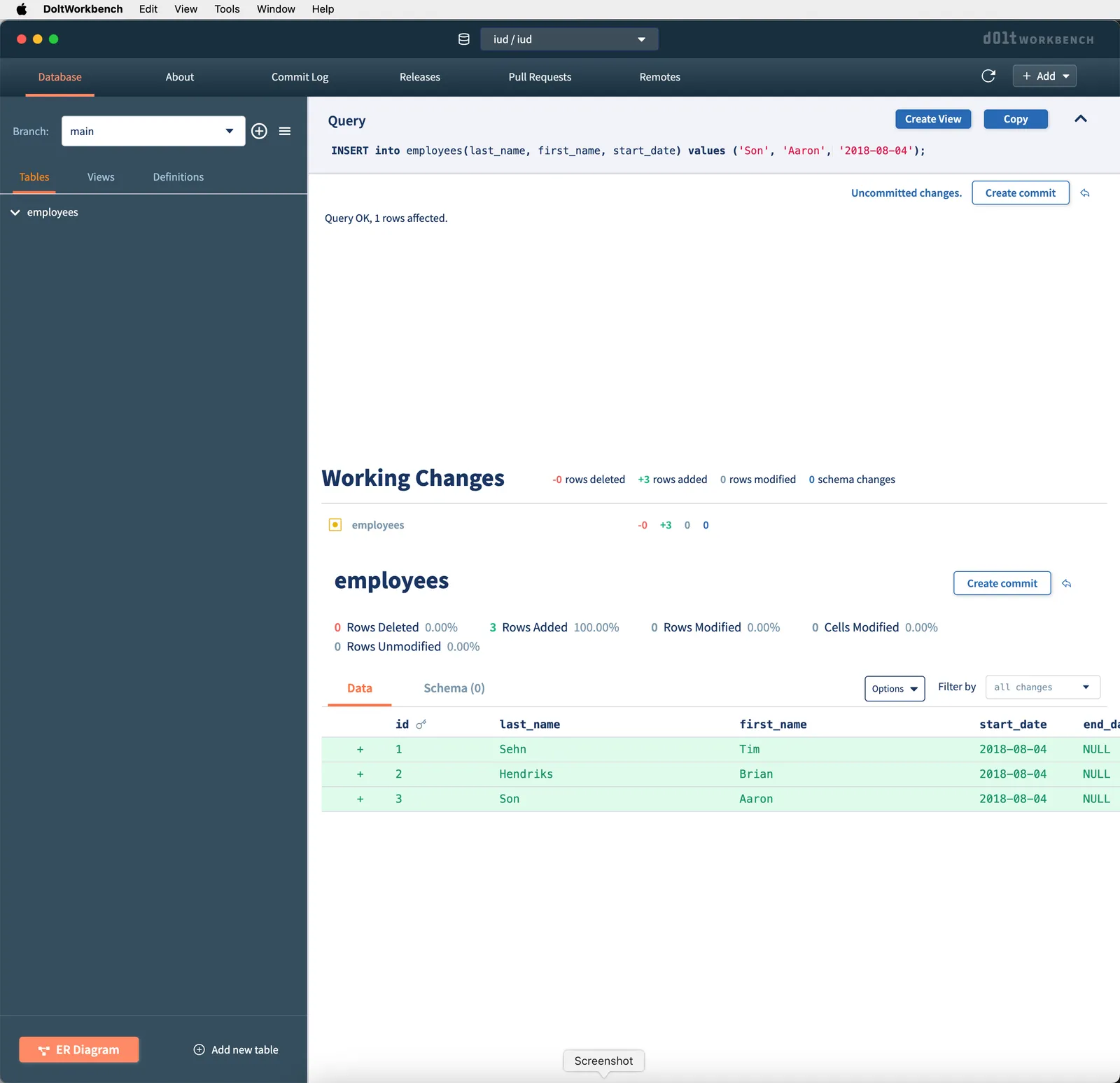
If we want to permanently mark this point in our version history, which we do, we create a Dolt commit using the “Create Commit” button. This also makes future diffs use this point as a reference which helps to show what we’ve done for this article. We have the opportunity to describe what we changed. I enter “Inserted Employees” and click “Commit”. I now have a commit in the log. You can read more about commits in this Dolt for Beginners article.
Update#
Now, we will change a row. We change existing rows using the UPDATE SQL query. Update statements take the general form:
UPDATE <table> SET <column> = <value> WHERE <condition>;As I am writing this article, I’ve decided to quit. This is my last day here at DoltHub. It’s been fun folks. To set the end date as today for my row I can run:
UPDATE employees SET end_date=curdate() where first_name='Tim' and last_name='Sehn';curdate() is a SQL function that returns the current date. I run this query by using the Dolt Workbench query box and clicking the play button. Just like last time, I get a helpful diff from Dolt to tell me what I’ve changed.
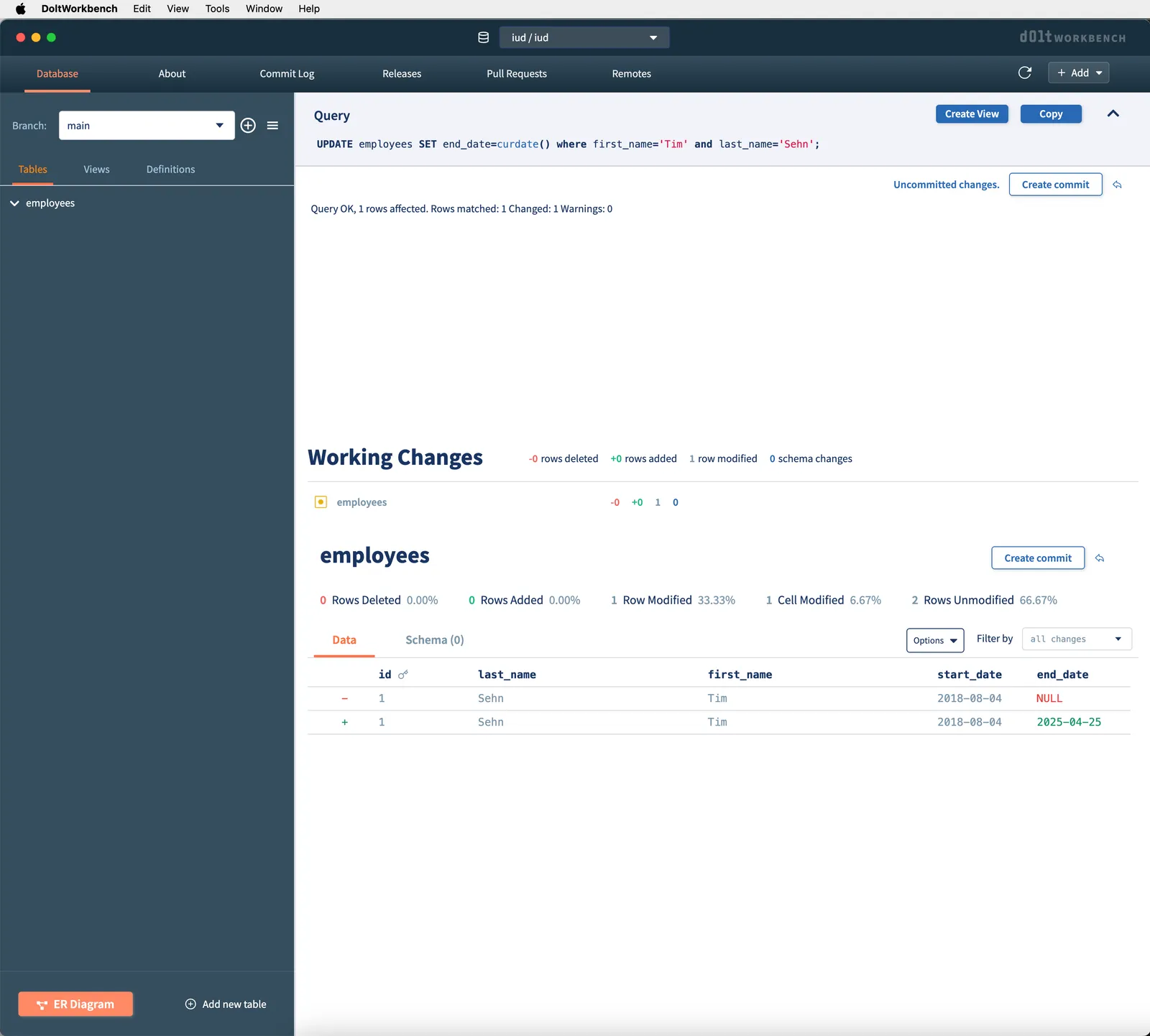
I will make a Dolt commit so I can use this point for the diff view for the next section.
Delete#
Finally, we will delete a row. We delete rows in SQL using the aptly named DELETE query. Delete statements take the general form:
DELETE FROM <table> WHERE <condition>;A lost employee is a shame on the company. I don’t want any record of employees who leave to exist (except in Dolt history). To delete all records with an end_date, I use the following query:
DELETE FROM employees where end_date is not NULL;Notice NULL values in SQL need to be treated differently than defined values. If I had instead put end_date = NULL, my query would have failed. I must use is NULL or is not NULL to compare to NULL. I can again run this query by using the Dolt Workbench query box and clicking the play button. Again I get a helpful diff from Dolt to tell me what I’ve changed.
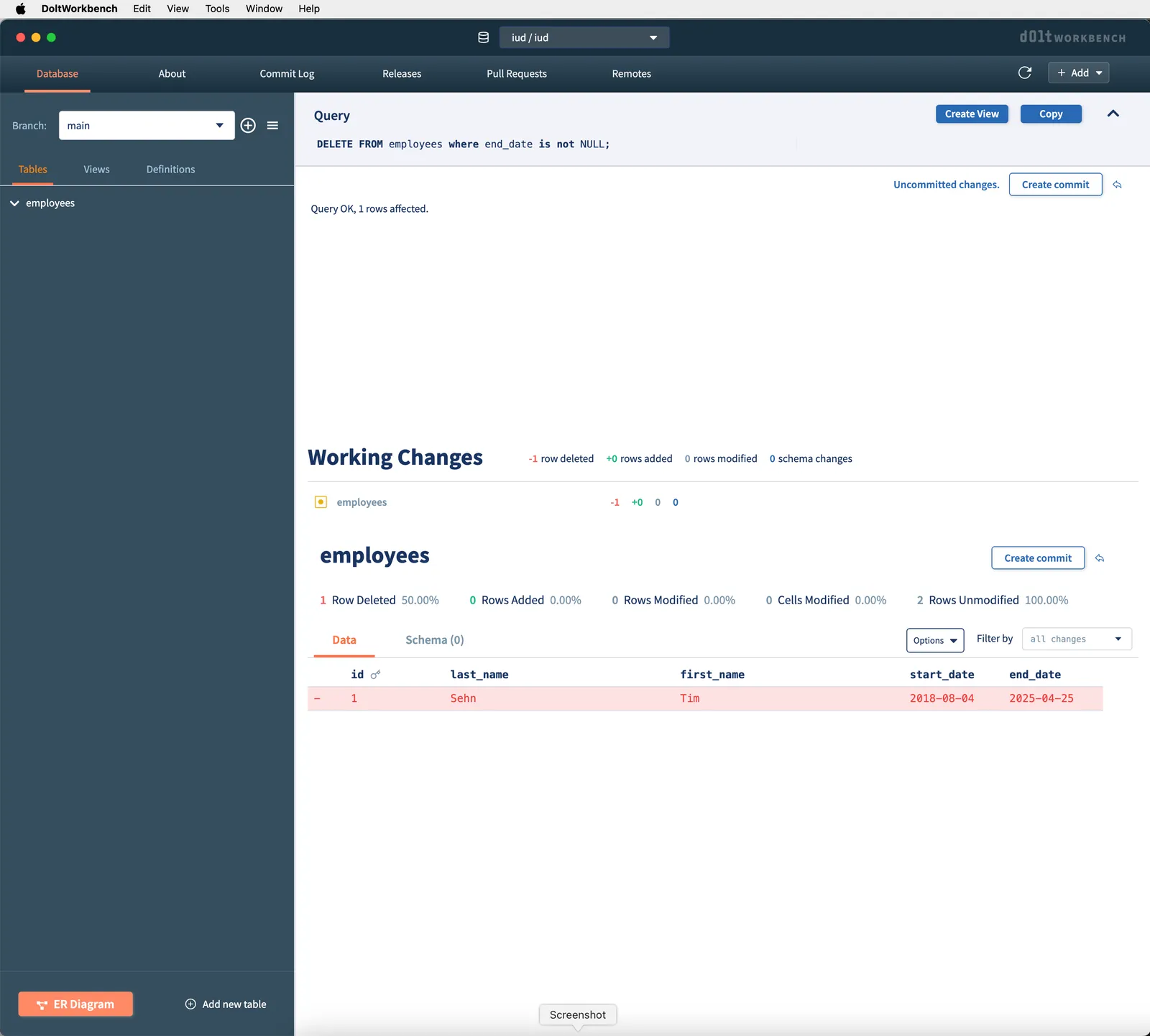
Conclusion#
You now know how to write basic INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE SQL queries and how to use them to change public data shared on DoltHub. Feel free to practice your SQL on the iud database you now have locally. More questions? Check out the rest of our Dolt for Beginners series or come by our Discord and ask us questions. We’re here to help.